Screened and Shielded Cables & Wires
Screened and Shielded Cables & Wires
Screened and shielded cables and wires are designed to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) in electrical and electronic systems. They are commonly used in applications where signal integrity is crucial, such as telecommunications, computer networks, audio/video systems, and industrial automation.
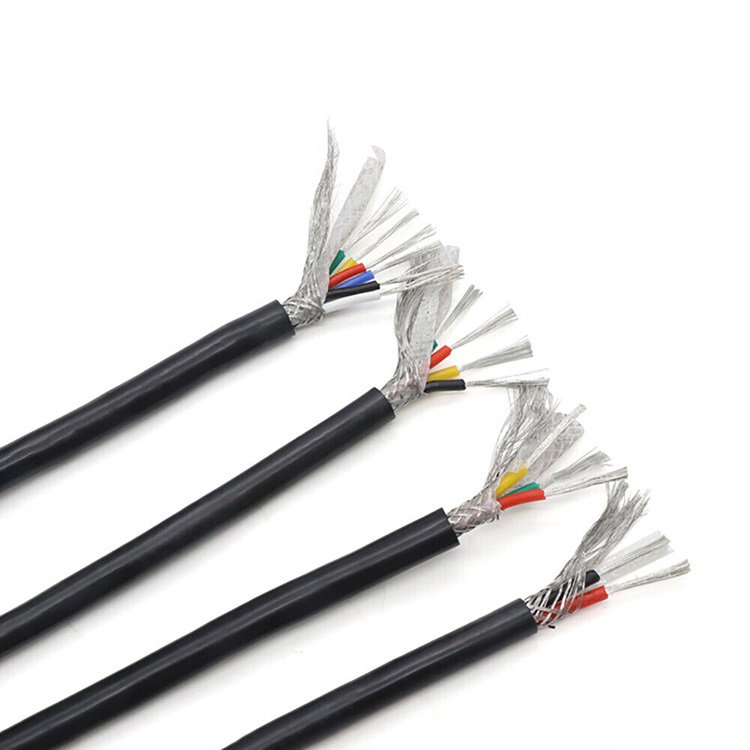
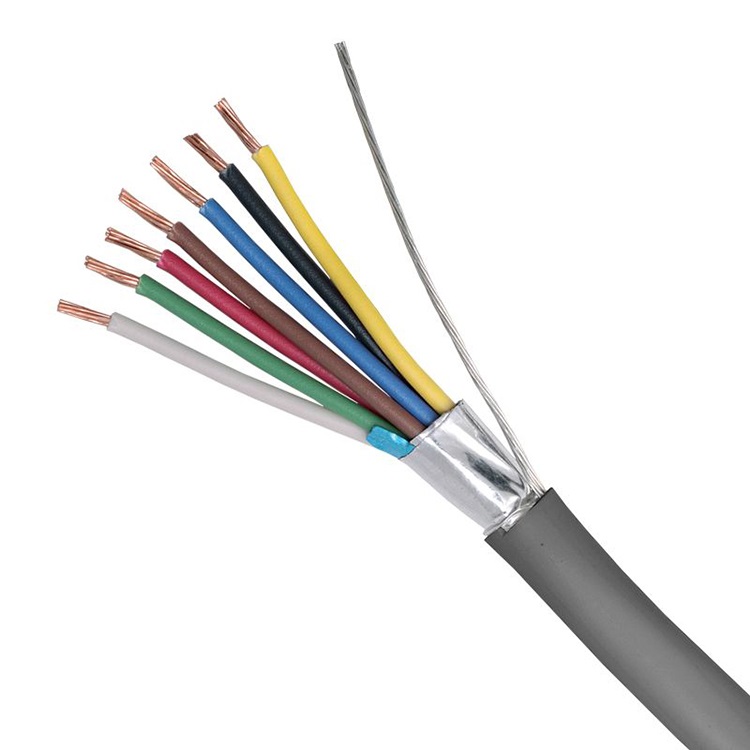
Screened Cables: Screened cables, also known as shielded cables, have an additional layer of shielding material wrapped around the conductors. The shielding layer is typically made of metallic materials such as copper or aluminum. The purpose of the shield is to protect the internal conductors from external electromagnetic fields and to prevent the emission of electromagnetic radiation from the cable.
The shielding in screened cables acts as a barrier, blocking external interference from entering the cable and reducing the electromagnetic radiation emitted by the cable. The shield is usually grounded to provide a path for the interference to dissipate, reducing its impact on the signals carried by the conductors. The shield can be a metallic foil or a braided mesh, and it is often covered with an insulating layer for protection.
Shielded cables are available in various configurations, such as coaxial cables (used for transmitting high-frequency signals), twisted pair cables (commonly used in data communications), and multi-conductor cables (used for carrying multiple signals or power lines).
Benefits of screened cables include improved signal quality, reduced crosstalk between adjacent cables, and enhanced resistance to external interference.
Shielded Wires: Shielded wires are similar to screened cables but consist of individual insulated conductors rather than a complete cable assembly. They are often used for shorter distances or in applications where flexibility is required.
Shielded wires typically have a metallic shield around each individual conductor, similar to the shields used in screened cables. The shields are grounded to provide protection against external electromagnetic fields and to minimize the effects of interference on the signals carried by the conductors.
Applications for shielded wires include data transmission, control systems, instrumentation, and audio connections. They are commonly found in environments with high levels of electromagnetic interference, such as industrial settings.
When selecting screened cables or shielded wires, factors to consider include the level of interference present in the environment, the required signal integrity, the frequency range of the signals, and the specific application requirements.
It is important to note that while screened cables and shielded wires can greatly reduce interference, they do not eliminate it entirely. Proper installation, grounding, and adherence to industry standards and guidelines are essential to maximize their effectiveness.